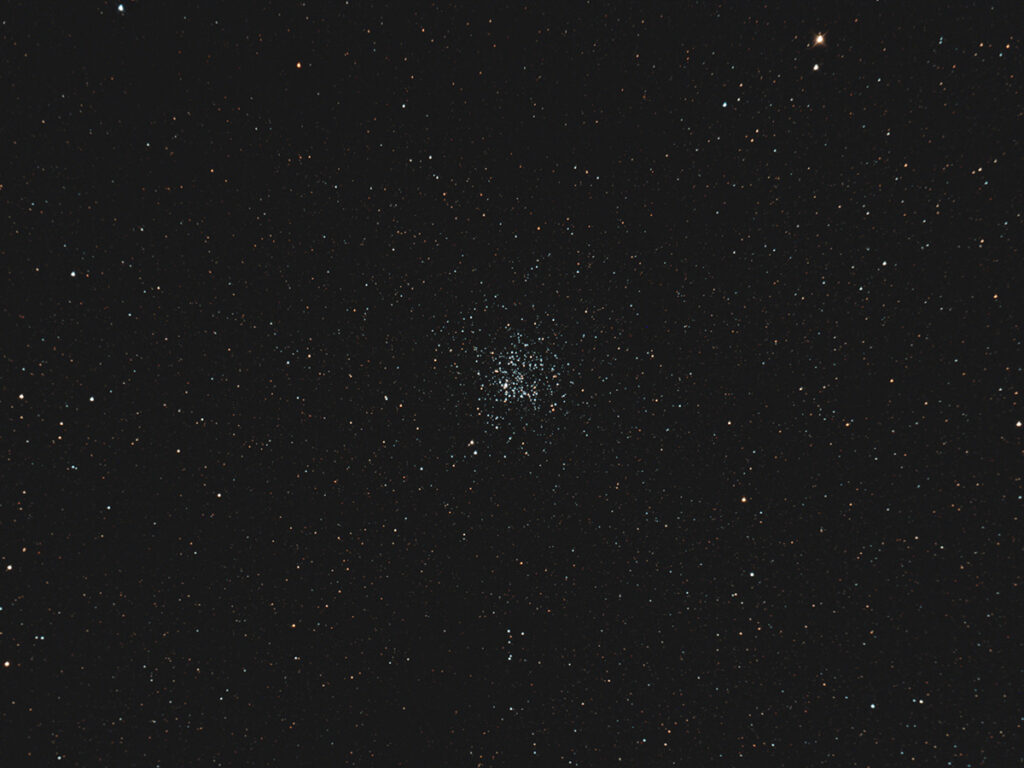

M11 – Open Cluster in Scutum
Telescope: Astro-Tech 8” f/8 Ritchey-Chretien, Orion Atlas EQ-G
Camera: Canon EOS Ra, Baader Mk III MPCC
Filter: Orion Imaging Skyglow Filter
Guide scope: Astro-Tech 60mm, Starlight Xpress Super Star, PHD2
Exposure: 21x60sec, ISO 800, saved as RAW
Darks: Internal (Long Exposure Noise Reduction On)
Flats: 32×1/20sec, Tee shirt flats taken at dusk
Average Light Pollution: Red zone, Bortle 8, poor transparency, haze
Lensed Sky Quality Meter: 17.8
Stacking: Mean with a 1-sigma clip.
White Balance: Nebulosity Automatic
Software: Backyard EOS, Deep Sky Stacker, Nebulosity, Photoshop
M11 is a bright and wonderfully rich open cluster just off the tail of Aquila. It is an easy binocular object that just gets keeps getting better in large telescopes. The cluster lies approximately 6000 light years away and contains an estimated 2900 stars in a volume of space about 20 light years across. The average distance between the stars in the cluster is about 1 light year, making this a very crowded neighborhood!
M11 is currently well placed in the southeast as the sky darkens.








Recent Comments