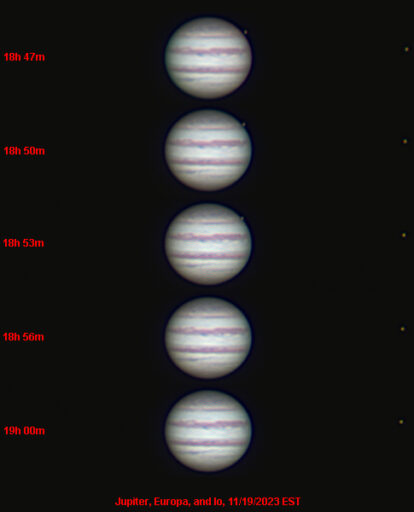
Telescope: Unitron 510 5” f/16 refractor, Atlas EQ-G
Camera: ZWO ASI 294MC
Filter: 2” Baader Fringe Killer (Minus Violet)
Exposure: 3min x 2.3ms, Gain 400, saved as RAW8/SER
Seeing: 3/5
White Balance: Nebulosity Automatic
Software: SharpCap Pro, Autostakkert, Registax, Nebulosity, Photoshop
This is from my second evening dedicated to evaluating the 510 for planetary imaging using a ZWO ASI294MC camera with SharpCap Pro. This is one of several sequences that I shot of Jupiter as it climbed higher in the east. Each sequence consisted of five 3 minute sets that were designed to be stacked in AutoStakkert, sharpened in Registax, and then de-rotated and combined in WinJuPos. During this particular sequence Europa slipped behind Jupiter with Io standing off to the right. This was such a neat event to watch I decided to show this as a stand-along sequence. This is a nice example of just how dynamic the Jovian system can be and how it can show significant changes in just a few minutes even with a small telescope.








Recent Comments